How Much Sleep Do I Need? B・SYNC Answers The Question

In today's day and age, getting a good night's sleep seems more challenging than ever. We live hectic lives, with the struggles of balancing work and home life now beset by numerous distractions such as electronic devices, social media, and 24-hour news cycles.
So, you may ask, "how much sleep do I need?" or more preciously ", how much deep sleep do I need?" "how much light sleep do I need?" or even "how much REM sleep do I need?"
The answers, unfortunately, are not so simple. Sleep needs vary from person to person and depend on numerous factors such as age, lifestyle, and health status. However, not getting enough sleep can significantly affect your physical and mental health, so finding your balance is essential.
In this article, we'll look at what the experts say about how much sleep you need. We'll explore light sleep, deep sleep and REM sleep. Then, we'll look at sleep deprivation and its causes, give you ten tips for getting better sleep and introduce you to wake-up tablets. Let's jump in!
How Much Sleep Do I Need?
As mentioned, "how much should I sleep" is not an easy question to answer. How much sleep you need each night depends on various factors. However, most experts agree that adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Factors contributing to how much sleep you need:
Age: As we age, our sleep needs change. For example, young children and teenagers need more rest than adults do.
Lifestyle: People who have physically demanding jobs or are regularly active need more sleep than sedentary people.
Health status: People with chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or depression may need more sleep than people without these conditions.
The National Sleep Foundation (NSF) recommends the following:
- Newborns (0-3 months): 14-17 hours
- Infants (4-11 months): 12-15 hours
- Toddlers (1-2 years): 11-14 hours
- Preschoolers (3-5 years): 10-13 hours
- School-age children (6-13 years): 9-11 hours
- Teenagers (14-17 years): 8-10 hours
- Adults (18-64 years): 7-9 hours
- Older adults (65+ years): 7-8 hours
It's important to note that these are averages, and some people may need more or less sleep than the suggested amounts.
Listening to your body and how you feel after a night's sleep is important. If you feel tired during the day, it may signal that you need to get more sleep.
How Much Should I Sleep: Light Sleep vs Deep Sleep vs REM Sleep
There are five stages of sleep that rotate between non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM). These include light sleep and deep sleep. Most people need a mix to feel rested and well-rested and cycle through different stages several times during the night.
How Much Light Sleep Do I Need?
Light sleep is the first and second stage of sleep, as well as REM. During these stages, your eye movements slow down, and your muscles relax. You may still be able to wake up easily at this point. It is lighter and less restful than deep sleep and most people spend about 50% of their time in light sleep.
How Much Deep Sleep Do I Need?
On the other hand, deep sleep is a more restful and rejuvenating type of sleep. It is the type of sleep you experience in the second stage of the sleep cycle. Most people spend about 10-15% of their time in deep sleep.
During this stage, your breathing and heart rate slow down, and your muscles relax even further. This is the most restful stage of sleep.
How Much REM Sleep Do I Need?
REM sleep is the final stage of the sleep cycle. It is lighter than deep sleep but more restful than light sleep. Most people spend about 20-25% of their time in REM sleep.
During this stage, your brain is active, and dreams occur. Your eyes may move rapidly as you dream. Your breathing and heart rate are also elevated during REM sleep. REM sleep is vital for your mental and emotional health. It helps you process and store memories and may help boost your mood and creativity.
What is Sleep Deprivation?

Sleep deprivation is when you do not get enough sleep. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
Acute sleep deprivation occurs when you miss a few hours of sleep, such as if you stay up late to finish a project or go to a party. Chronic sleep deprivation occurs when you consistently don't get enough sleep, such as if you have difficulty falling asleep or wake up frequently during the night.
Sleep deprivation can have severe effects on your health. It can make it difficult to concentrate, remember things, and make decisions. It can also lead to moodiness and irritability. In extreme cases, it can even cause hallucinations and delusions.
The Physical Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can have several physical consequences. It can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of diabetes and heart disease. It can also make you more likely to get sick and impair your immune system.
Sleep deprivation can also cause accidents. A lack of sleep can make concentrating and paying attention difficult, leading to mistakes.
The physical signs of sleep deprivation include:
- Yawning
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Blurred vision
Alongside the physical problems that lack of sleep can cause, it can also significantly impact your mental health.
The Mental Health Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can have mental health consequences. It can cause anxiety, depression, and mood swings. It can also make you more forgetful and can impair your decision-making ability.
In extreme cases of sleep deprivation affecting mental health, it can even lead to psychosis. This is a condition characterised by delusional thinking and hallucinations.
The mental health signs of sleep deprivation include:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Forgetfulness
- Impaired decision-making
Now that we've seen the issues that lack of sleep can cause, let's look at why.
10 Causes of Sleep Deprivation and Insomnia

There are many different causes of insomnia. Some people have difficulty falling asleep because of stress or anxiety. Others may have medical conditions that make it difficult to sleep.
Some common causes of insomnia include:
Stress: Stress can be caused by work, family, or financial problems.
Anxiety: Anxiety is often caused by worry, stress, or fear.
Depression: Depression can be caused by traumatic events, major life changes, medical conditions, or imbalances in your brain.
Medical conditions: Many medical conditions can cause insomnia. These include sleep apnea, allergies, arthritis, asthma, cancer, heart disease, and thyroid problems.
Medications: Some medications can also cause insomnia. These include antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and stimulants.
Stimulants: Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can all make it difficult to fall asleep. They are found in coffee, tea, soda, cigarettes, e-cigs and more.
Light: Exposure to light can make it more difficult to fall asleep. This is because light suppresses the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps you sleep.
Noise: Noise can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. It can be caused by traffic, loud music, or other disruptive sounds.
Temperature: A too-warm or too-cool room can cause insomnia. The ideal sleeping temperature is between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit.
Work schedule: A schedule involving shift work or early mornings can make sleeping difficult. This is because it can disrupt your natural sleep cycle.
Common Treatments for Sleep Deprivation and Insomnia
There are many different treatments for sleep deprivation and insomnia. The most important thing is to find the cause of the sleep problem and treat it.
Some common treatments for sleep deprivation and insomnia include:
- Cognitive behavioural therapy: This therapy can help you change your thoughts and behaviours around sleep.
- Relaxation techniques: These techniques can help you to reduce stress and anxiety. They include yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
- Sleep hygiene: This involves changing your lifestyle and habits to promote better sleep. These changes can include exercise, a regular sleep schedule, and avoiding caffeine before bed.
- Stimulus control therapy: This therapy involves changing your environment to promote better sleep. This can include making your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
- Medications: Many different types of medicines can be used to treat insomnia. These include over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, and natural remedies.
If you are having trouble sleeping, you must talk to your doctor. They can help you to find the cause of your sleep problems and treat them.
Considering Sleep Inertia
It's important to note that even if you've had enough sleep, you may still feel groggy and tired when you first wake up. This is because of something called sleep inertia.
Sleep inertia is the feeling of being groggy and disoriented after waking up. It can last from a few minutes to a few hours. Sleep inertia is caused by the body's natural sleep cycles. When you first wake up, your body is in a light sleep stage. This means that you may not be fully awake and alert.
Sleep inertia can be a problem if you must be awake and alert immediately, such as if you must go to work or school. It can also be a problem if you are driving.
There are a few things you can do to reduce sleep inertia:
- Get out of bed and move around. This will help to wake up your body and mind.
- Eat a healthy breakfast. This will give you energy and help to wake up your body.
- Drink coffee or another caffeinated beverage. This will help to increase your alertness.
- Take a shower. This will help to wake up your body and mind.
- If you are feeling sleepy, it is essential not to drink alcohol. Alcohol can make you feel drowsy and increase the effects of sleep inertia.
It's also important to avoid driving if you are feeling sleepy. If you must drive, stop for a break every two hours.
10 Tips For Getting Better Sleep

If you are having trouble sleeping, there are many things you can do to improve your sleep. Here are ten tips for getting better sleep:
Follow a regular sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This will help to regulate your body's natural sleep rhythm. It can be more difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep without a regular sleep schedule.
Create a bedtime routine: A bedtime routine can help to signal to your body that it is time to sleep. This can include taking a bath, reading a book, or doing relaxation exercises. Take some time to relax and clear your mind. Perhaps choose a calming book or pick some music with a slow tempo.
Avoid stimulants before bed: Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake. It is best to avoid caffeine in the late afternoon and evening. While alcohol may make you sleepy, it can disrupt your sleep. It can cause you to wake up during the night or have difficulty falling back asleep. Finally, nicotine is another stimulant that can keep you awake. It is best to avoid tobacco products in the late afternoon and evening.
Avoid eating large meals before bed: Eating a big meal can cause indigestion and make it difficult to fall asleep. It is best to eat a light evening meal or snack.
Avoid exercise before bed: Exercise can energise you and make it difficult to fall asleep. It is best to avoid strenuous activity for at least three hours before bedtime.
Create a comfortable sleep environment: Your bedroom should be dark, silent, and at a low temperature. This will help you to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. Be sure to have comfortable sheets and pillows that support your body. This will help you to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Limit exposure to blue light before bed: Blue light can disrupt your natural sleep rhythm. It is best to avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime.
Practice some relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and prepare for sleep. Some relaxation techniques include deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualisation.
Get out of bed if you can't sleep: If you cannot fall asleep after 20 minutes, it is best to get out of bed and do something else until you feel sleepy. This will help to prevent you from getting frustrated and stressed about not being able to sleep.
Consider medication: If you have tried all of the above tips and are still struggling to sleep, you may want to consider medication or supplements. However, there may be a twist!
You've undoubtedly heard of sleeping tablets, but what about wake-up tablets?
Introducing Wake-Up Tablets
When people ask, "how much should I sleep?" they ignore one crucial part of the whole sleep routine: waking up. How you wake up can colour the whole of your day and how you feel. A poor wake-up can leave many people believing they haven't had enough sleep.
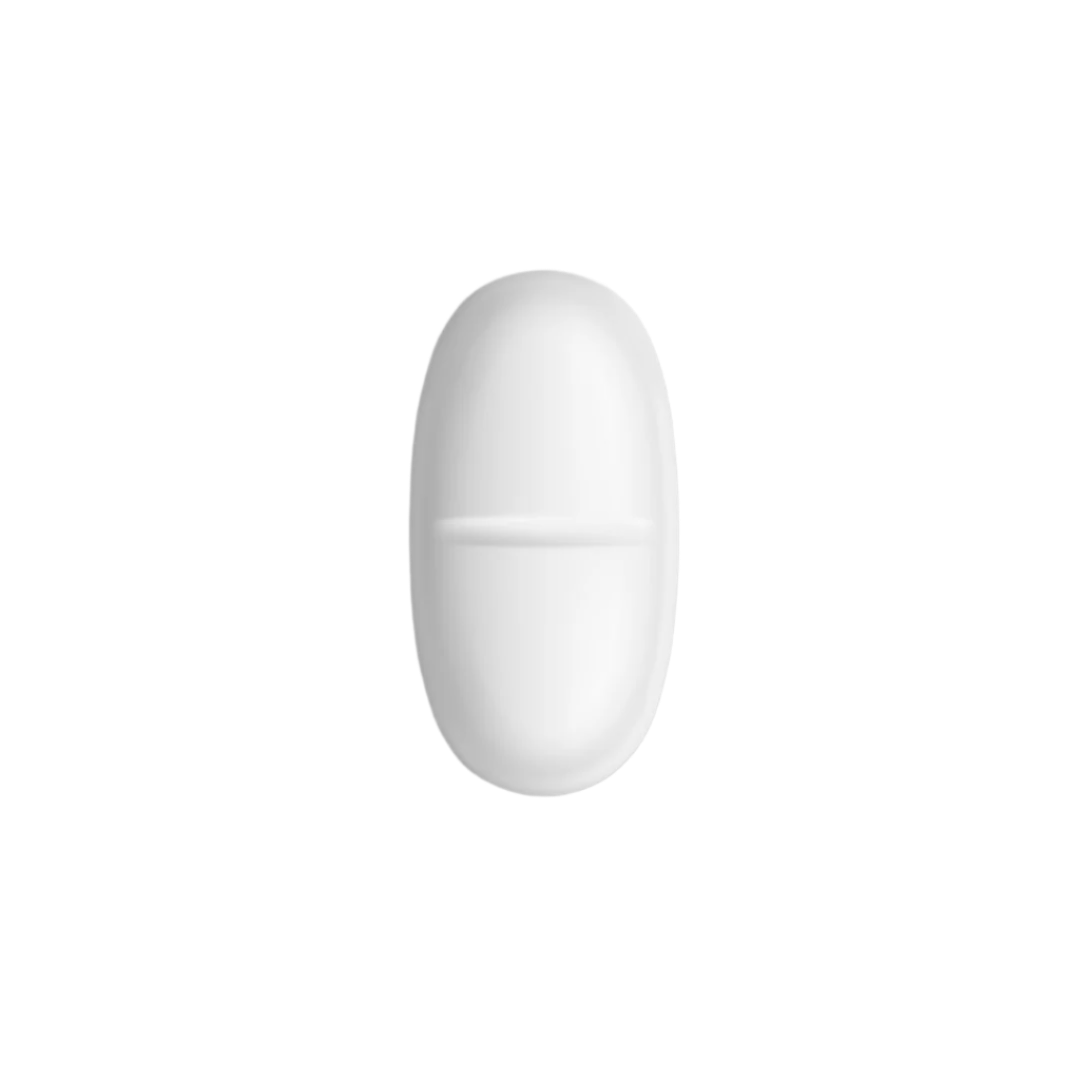
Wake-up tablets are designed to help you wake up with ease and our own B・SYNC ON is the first such tablet on the market. Our wake-up tablets can be helpful if you have trouble getting out of bed in the morning or or want to feel in a better mood.
Sleeping Tablets vs Wake-Up Tablets
The main difference between sleeping tablets and our wake-up tablets is, quite simply, how they affect you.
Sleeping tablets are designed to make you drowsy so that you can fall asleep more easily. They usually contain ingredients like melatonin, which is a hormone that makes you feel sleepy. Some people are wary of taking sleeping tablets as they can be addictive and may cause side effects like drowsiness and headaches.
On the other hand, B・SYNC ON is designed to help you feel refreshed and energised. The tablets contain caffeine, B vitamins and zinc. This combination helps reduce feelings of tiredness so you can be more sociable in the morning and have more energy throughout the day. B・SYNC ON is the first wake-up supplement clinically tested and proven to work, and uses innovative and patented delayed-release technology.
Waking up is an important part of getting a good night's sleep. If you have trouble with your energy levels after sleep, or find yourself struggling to get going, then our wake-up tablets may be worth considering.
Conclusion
If you want to know "how much should I sleep?" then the answer is: it depends. Everyone is different and everyone needs different amounts of sleep. However, in most typical cases people need around 7-9 hours in bed. How much sleep you need, how you sleep, and how you wake up can all affect how well-rested you feel.
One way to help ensure you wake up feeling refreshed and energised is to take a wake-up supplement like B・SYNC ON. B・SYNC ON contains caffeine, B vitamins, and zinc, which have all been clinically proven to reduce feelings of tiredness. Try B・SYNC ON if you're looking for a morning energy boost!
FAQs
How much sleep do I need?
Most people need around 7-9 hours of sleep per night. However, everyone is different, and some people may need more or less sleep.
How can I tell if I'm getting enough sleep?
If you're consistently waking up feeling tired, then you may not be getting enough sleep. Another way to tell is to pay attention to how you feel during the day. If you're struggling to concentrate or getting irritable, this could be a sign that you're not getting enough rest.
What are the consequences of not getting enough sleep?
Not getting enough sleep can lead to many problems, including difficulty concentrating, irritability, and impaired judgment. Sleep deprivation can increase your risk of developing obesity, heart disease, and diabetes in the long term.